Theme: Evolving Landscape of Epigenetics & Therapeutic Approaches for Human Diseases
Human Diseases 2020
ME Conferences humbly invites all the Epigenetics, Genetics and Oncology researchers, scientists and students from all over the world to attend “2nd International Conference on Epigenetics and Human Diseases" during July 15-16, 2020 at Helsinki, Finland.
Epitranscriptomics is about the structure and function of molecular level genes and it is a relatively new field in the world of genetics. Human genetics is the field of biology that deals with the study of inheritance that occurs in humans and is referred to as genetic diseases due to any mutation or changes in genes. Today gene editing can be used to treat some of the genetic diseases in various ways. It also deals with the study of chromosomes and an organism's gene expression may give insight into an inheritance, genetic variation and mutations.
The main theme of the Human Diseases 2020 conference is: “Analysis of the gene expression system for the epigenetic regulation" which is all about simplifying the complex phenomenon behind Epigenetic mechanism & protein expression and it gives knowledge about transcriptomes in health and diseases & it gives a clear explanation of the principle genome.
Why to Attend Epigenetics and Human Diseases?
Human Diseases 2020 Conference is a novel discourse to join together in generally identified scholastics in the field of hereditary qualities and atomic science Analysts, Open prosperity specialists, Researchers, Scholastic analysts, Industry masters, Researchers to exchange their knowledge about the research.
The point of this gathering is to provide the latest views for treatment that will be valuable over the range of Epitranscriptomics. Importantly, changes in core-regulators of the epitranscriptomes are related to many diseases of human or congenital disorders. It Is Also a Great chance to meet with Members across the World Related Associations, and Societies.
Why Epigenetics and Human Diseases in Finland:
The finest way of travel to Finland’s fascinating history is over a tour of its cities. One such city, Visitors can see this history for themselves in its big architecture and leftovers at Turku Castle and the Aboa Vetus and Ars Nova Museum. when Russia gained control of the country, Helsinki has become the capital city, and till today relics as the capital. It also companies many historical sites. Finland famous for its numerous lakes, Tampere is the major city on the Finnish Lakeland. Finland is likewise identified to have outstanding water quality, and green deep woods and forests about the sea, rivers, and the waterways.
Target Audience of Epigenetics and Human Diseases:
Our organization takes immense pleasure in welcoming,
- Epigenetics, Genetics and Oncology Researchers
- Genetic Counsellors
- Bioinformatician
- Human Genetics/ Epigenetics/Cancer Associations and Society
- Molecular Biologists
- Business delegates
- Directors, Board Members, Presidents, Vice Presidents
- Cell Biologists
- CEO's and R&D Heads from Industries
- Business Entrepreneurs and Industrialists
- Human Genetics Researchers
- Pharmacists
- Drug Manufacturing Companies and Industries
- Laboratory Technicians and Diagnostic Company
Track 1: Epitranscriptomics for Biomedical Discovery
The latest growing field is Epitranscriptomic related to the entire delineation and elucidation of chemical modifications of nucleotides contains within all classes of RNA that do not involve in the ribonucleotide sequence change. There is a number of diverse and different nucleotide modifications that have been identified in RNA, dwarfing the number of nucleotide modifications found in DNA. The majority of epitranscriptomic modifications have been identified in ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, and small nuclear RNA. The rapid advancement of nextâ€generation sequencing and mass spectrometry technologies have allowed for the identification and functional characterization of nucleotide modifications in both proteinâ€coding and nonâ€coding RNA on a global, transcriptome scale.
- Immunological disease
- Drug addiction
- Mining the epitranscriptome
- NGSâ€based RNA modification techniques
- Physiological functions of RNA modifications
- RNA splicing
Track 2: Epigenetic Biomarkers
Biomarkers are playing an important role and taking a high risk by patients screening with developing cancer, diagnosing patients with dangerous tumors at the earliest possible stage, establishing an accurate prognosis, and predicting and observing the response to specific therapies. For cancer Epigenetic alterations are innovative biomarkers, because of their stability, frequency, and noninvasive accessibility in bodily fluids. As therapeutic targets, Epigenetic modifications are also reversible and potentially useful.
- Behavioural epigenetics
- DNA methylation
- Cancer biomarkers
- Molecular biomarkers
Track 3: Epigenetics
Epigenetics is all about the heritable changes in gene expression, which do not involve any changes to the underlying DNA sequence, without a change in genotype a change in phenotype, which in turn affects how cells read the genes. There is a possibility for the natural occurrence of Epigenetic change and it can also be influenced by several factors including age, the environment or lifestyle, and disease state. More damaging effects held by the Epigenetic change, which can result in diseases related to cancer.
- Epigenetic mechanisms
- Genomes and epigenomes
- Computational epigenetics
- Cigarette smoking and epigenetics
Track 4: Pharmacogenomics & Personalized medicine
Pharmacogenomics latest researches have made it possible to understand the reasons behind the different responses of a drug. The basis for recommending a drug and its dose to an individual patient is provided by the Discovery of genetic variants and its association with the varying response of drugs. To improve the outcome of the treatments and also to reduce the risk of toxicity and other adverse effects genetic makeup-based prescription, design, and implementation of therapy are useful. Trial and error approach of treatment is avoided by a better understanding of individual variations and their effect on the response of drug, metabolism excretion, and toxicity.
- Methylation inhibiting drugs
- Bromodomain and inhibitors
- Histone catalyse (HAT) inhibitors
- Protein methyltransferase inhibitors
- Epigenetics meets endocrinology
- Future direction of epigenetic drugs
Track 5: Clinical Epigenetics
Clinical epigenetics is useful for techniques of molecular biology detecting alterations in DNA methylation in histone modification to diagnose and heritable defects in the gene or genome expression are helpful in the study disorders characterized. Disorders of imprinting, chromosomes uniparental inheritance and chromosome segments, and somatic epigenetic anomalies in cancers are included applications.
- Epigenetic drugs
- Prospects for epigenetic therapy
- Clinical study of epigenetics and epitranscriptomics
- Psychopathy
- Social behaviour of insects
Track 6: Current Case Study in Epigenetics and Epitranscriptomics
It is the knowledge of epigenetics, combined with grows of technologies such as CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing and next-generation sequencing. In recent years, it permits us to superior recognize the interaction between epigenetic alter, quality direction, and human diseases, and will lead to the improvement of unused approaches for atomic determination and focused on clinical range molecular medicines. The catalyzing adoption of epigenetics or epitranscriptomics methods are helpful to understand the basic biology and human diseases. The new technologies coupled with the advancement of current approaches and it will allow for the new therapies development and immunotherapeutic targets for human diseases associated with deficient RNA modification.
- Cell types
- Viral vectors
- Human genetic engineering
Track 7: Plant Epigenetics
In epigenetic regulation plants are masters. By using plants most of the major epigenetic mechanisms known to occur in eukaryotes. In-plant genomes due to CG, CHG, and CHH sequence contexts DNA methylation occurs, in patterns that reflect a balance between enzyme activities that install, maintain or remove methylation. As in other eukaryotes, histone-modifying enzymes influence epigenetic states in plants and these enzymes are encoded by comparatively large gene families, allowing for diversified as well as overlapping functions. RNA-mediated gene silencing is accomplished using multiple distinct pathways to combat viruses, tame transposons, orchestrate development, and help organize the genome. Plants with a multi-layered and robust epigenetic circuitry are provided because of the interplay between DNA methylation, histone modification, and noncoding RNAs.
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Coding DNA
- Crop epigenetics: hybridization and heterosis
- Natural variation and ecological epigenetics
- Heritability of epigenetic marks
Track 8: Translational Epigenetics
Cancer epigenetics research is now showing interest in Translational epigenetics. A range of different epigenetic marks can activate or repress gene expression. Epigenetic dysregulation can also have a causal role in cancer etiology, while epigenetic alterations are associated with most cancers. An early role in neoplastic transformations could be presented by epigenetically disrupted stem or progenitor cells, while perturbance of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression in cancer-relevant pathways will also be a contributing factor. The activity of key cancer genes and pathways can be regulated as a therapeutic approach has a possibility by the reversibility of epigenetic marks. The epigenome functioning can affect a range of chemical agent's availability of growth has led to a range of epigenetic-therapeutic approaches for cancer and intense interest in the second-generation epigenetic drugs development (epi-drugs development) which would have greater specificity and efficacy in clinical settings.
- Genomic variation in human
- Cancer genomics
- Cancer genome sequencing
- Cancer epigenetics
Track 9: Role of Epigenetics in Biology and Human Diseases
Genetic causes for human disorders are being discovered at a first-time pace. The changes in the epigenomics or in the abundance and proteins activity involved in increasing subclass of disease-causing mutations that regulate the structure of chromatin. The direct changes in epigenetic marks, such as DNA methylation, commonly found to affect imprinted gene regulation are the reason for disease. The effect either chromatin in trans or have a cis effect in altering chromatin configuration is due to the disease-causing genetic mutations in epigenetic modifiers.
- Stem cells
- Autoimmune disease
- Behaviour plasticity
- Microbial epigenetics
Track 10: Epigenetics and Metabolism in Health and Disease
Molecular rewiring of cancer cells facilitating cancer development and progression affected by epigenome alterations and metabolism effect. Modulation of histone and DNA modification enzymes occurs owing to metabolic reprogramming driven by oncogenes and expression of metabolism-associated genesis, in turn, epigenetically regulated, promoting the well-known metabolic cancer cells reprogramming and, consequently, altering the metabolome.
- Epigenetics in human neurodevelopmental disorders
- Epigenetic regulation of gene expression
- Epigenetics in human disease prevention
- Epigenetics in reproductive health
- Epigenetics in cardiovascular disease
- Epigenetics in nervous system
- Epigenetics modification
Track 11: Epigenetic Clock and Aging
The human health span and lifespan have been difficult to extend by identifying and validating molecular targets of interventions, as most clinical biomarkers are not sufficiently representative of the fundamental mechanisms of aging to serving as their indicators. In a latest research, aging centred on DNA methylation data from biomarkers has aided accurate age estimates for any cell tissue across the entire life course. These ‘epigenetic clocks’ link developmental and maintenance processes to biological aging.
- Epigenetic clock
- Epigenetic memory
- Epigenetic changes in aging
- DNA methylation changes during aging
- Histone modification changes during aging
Track 12: Animal Epigenetics
For the study of epigenetic mechanisms, animal models are essential. Researchers must provide the requisite accessibility to sensitive stages of pre- and postnatal development, growth and maturation, and events that approach senescence and death, where organisms are particularly sensitive to epigenetic changes, and provide a fair experimental window for evaluating a wide range of outcomes. During development, all vertebrate organisms control differentiation and growth using epigenetic mechanisms, so it is no wonder that significant changes in their spatial and temporal programming will have a profound impact on the outcomes of life-stages.
- Animal cloning epigenetics
- Animals models in epigenetic research
- Animal epigenetics examples
- Animal epigenetics welfare
Track 13: Cytogenetics
Genetics has a branch called Cytogenetics that is about the DNA structure within the cell nucleus. This DNA is condensed while the division of cells and form chromosomes. The cytogenetic is regarding the number and morphology of chromosomes, the physical location of genes on chromosomes, and chromosomal behaviour and chromosomal abnormalities in processes such as cell division. In most body cells with the exception of cells of reproductive and others such as the liver are always constant due to the morphology of chromosomes in a cell of a particular species.
- Molecular cytogenetics
- Cytotaxonomy
- Cancer cytogenetics
- Fluorescent in situ hybridization
Track 14: Chromatin and Chromosome Dynamics
The chromosome is a molecule of DNA, which consists either part or all of the genetic material is present. To form the Chromosome the condensation of Chromatin is used. Several factors affect the Chromatin structure. Based upon the Cell Cycle stage the overall structure depends. The many protein-coding expression patterns genes are arranged in response to exogenous stimuli, as well as cell-type-specific developmental programs.
- DNA packaging
- Chromosome biology in agriculture
- Homo and hetero chromosome
- Autosomal chromosomes
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- Karyotyping
Track 15: Environmental and Nutritional Epigenetics
Environmental epigenetics defines how cellular epigenetics and human health affected by environmental factors. To regulate gene expression epigenetic marks alter the spatial chromatin conformation. Environmental factors with epigenetic effects include behaviour, nutrition, and chemicals and industrial pollutants. During the development of utero and at the cellular level epigenetic mechanisms are also implicated, so environmental exposures may harm the fetus by impairing the epigenome of the developing organism to modify disease risk later in life.
- Epigenetic effects of environmental exposures
- Toxicoepigenetics
- Epigenetics and environmental origins of cancer
- Diet and the epigenome
Track 16: Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance
The epigenetic markers transmission from one organism to the next is Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance that without alteration of the DNA primary structure that is the nucleotides sequence disturbs the traits of offspring. The term 'epigenetic inheritance' may cover both cell-cell and organism–organism transfer of information. In multicellular organisms, they may have different mechanisms and evolutionary differences. These two levels of epigenetic inheritance are same in unicellular organisms.
- Putatively adaptive effects
- Inheritance of epigenetic marks
- Deleterious effects
Track 17: Epigenetics Market Products and Instrumentation
The global market of epigenetics is segmented on the basis of technologies such as DNA methylation, histone modification, and other technologies. The technology of methylation of DNA is the most widely accepted and it consists of great potential in the personalized drug development field and understanding of functional mechanisms in complex cases of the disease.
Instruments used in epigenetics are:
- Mass spectrometers
- Next-generation sequencers
- qPCRs
- Sonicators
Epigenetics Products are:
- Enzymes
- DNA Polymerases
- DNA Ligases
- Other DNA-modifying Enzymes
- Kits & Assays
- Bisulfite Conversion Kits
- Immunoprecipitation Kits
- Chip-Sequencing Kits
- Deep Sequencing Kits
- Methyltransferase Assays
- Histone Assays
- Reagents
- Buffers
- Histones
- Antibodies
- Magnetic Beads
- Primers
- Other Epigenetics Reagents
Global Epigenetics Market Research Report 2019-2023
With epigenetic modification, the occurrence of cancer and other diseases will drive Epigenetics market growth, in 2020 the global epigenetics market is expected to reach $12.8 Billion.
Based on the application market, oncology was the main application market, with revenue valued at over USD 3.07 billion. Some factors proposed to its market position that is growing prevalence of cancer with epigenetic modification base and strong product pipeline are.
The North America Microbiome Market will continue to be the largest market throughout the forecast period and accounting for over 41.0% of the overall revenue, Asia is expected to be a quickly increasing region with a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 12.4% over 2016-2020.
In the year 2018, the market of the Human Microbiome was valued at USD 351.81 million. Over recent years, the human microbiome market has been witnessing considerable growth on the back of rising incidences of diabetes, growing geriatric population, and continuous research and development conducted by pharmaceutical manufacturers and academia. In addition, a growing sedentary lifestyle, increasing incidence of diabetes and chronic diseases globally have contributed to the growth rate of the Human Microbiome market.
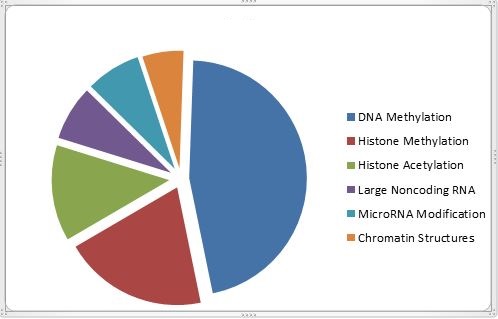
GLOBAL EPIGENETICS MARKET REVENUE SHARE (%) BY TECHNOLOGY
DNA Methylation is expected to hold the Largest Share over the Forecast Period in technology and the epigenetics market is dominated by DNA methylation, as it is the covalent addition of a methyl group in cytosine ring, which leads to the inhibition of transcription.
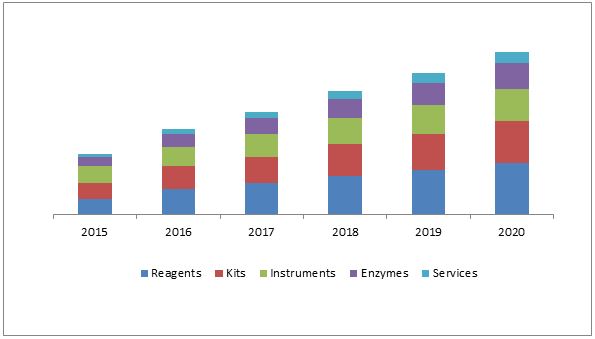
EPIGENETIC MARKET BY SIZE AND BY TYPE
In the year 2017 the global epigenetics market size was valued at USD 5.25 billion. It is estimated to register a CAGR of 19.7% during the forecast period. The increasing prevalence of cancer and other chronic diseases along with the rising geriatric population is poised to bolster the growth of the market
Related Societies
Europe Societies
- Clinical Epigenetics Society
- The Epigenetics Society
- Association of Clinical Cytogeneticists
- British Society for Human Genetics
- Clinical Genetics Society
- Clinical Molecular Genetics Society
- Genetics Society
- Human Genetics Commission
- Austrian Society for Human Genetics
- Belgian Society for Human Genetics
- Czech Society of Medical Genetics
- Danish Society of Medical Genetics
- Dutch Association of Clinical Genetics
- Finnish Society of Medical Genetics
- French Society of Human Genetics
- European Society for Medical Oncology
- European Oncology Nursing Society
- European Association for Cancer Research
- European Society of Human Genetics
- European Genetics Foundation
- European Cytogeneticist Association
- European Society of Gene Therapy
- Clinical Molecular Genetics Society
USA Societies
- American Cancer Society
- Haematology/Oncology Pharmacy Association
- American Association for Cancer Research
- Association of International Cancer Research
- International Agency for Research on Cancer
- American Society of Human Genetics
- National Society of Genetic Counsellors
- American College of Medical Genetics
- American Board of Genetic Counselling
- American Board of Medical Genetics
- Nation Coalition for Health Education in Genetics
- International Society of Nurses in Genetics
- Association of Genetic Technologists
- Genetic Society of America
Asia and Middle East Societies
- Australian Epigenetics Alliance
- Asian Clinical Oncology Society
- Asian Oncology Nursing Society
- Asian Society of Gynecologic Oncology
- Asian Society for Neuro-Oncology
- East Asian Union of Human Genetics Societies
- Association of Chinese Geneticists in America
- Hong Kong Society of Medical Genetics
- Japan Society of Human Genetics
- Genetics Society of Korea
- Korean Society of Human Genetics
- Genetics Society of Vietnam
- Turkish Association of Medical Genetics
- Japan Society of Gene Therapy
- American Human Geneticists of Indian Subcontinent Origin
- Stem Cell Society of India
Conference Highlights
- Translational Epigenetics
- Role of Epigenetics in Biology and Human Diseases
- Epigenetics and Metabolism in Health and Disease
- Epigenetic Clock and Aging
- Animal Epigenetics
- Cytogenetics
- Chromatin and Chromosome Dynamics
- Environmental and Nutritional Epigenetics
- Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance
- Epigenetics Market Products and Instrumentation
- Epitranscriptomics for Biomedical Discovery
- Epigenetic Biomarkers
- Epigenetics
- Pharmacogenomics & Personalized medicine
- Clinical Epigenetics
- Current Case Study in Epigenetics and Epotranscriptomics
- Plant Epigenetics
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 15-16, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Genetic Syndromes & Gene Therapy
- Journal of Stem Cell Research & Therapy
- Journal of Cell Science & Therapy
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by